The process of finding the gradient or derived function is called differentiation. There is a way of doing this called differentiating from first principles and this is studied in more detail in Year 12.
A quicker way to differentiate polynomial funtions and terms is to use a formula or rule.
For a function f(x) the derived function is given by f '(x).
An alternative notation is that for a function y the derived function is y ' or ![]()
The rule is:
|
The derivative of axn = naxn − 1
|
In words this says that to find the derivative of a term:
"multiply the coefficient by the exponent and then lower the exponent by 1."
|
Example 1
|
Example 2
|
Example 3
|
Example 4
|
|
| Differentiate |
x3
|
6x4
|
5x
|
23
|
| Answer |
3x²
|
24x3
|
5
|
0
|
Differentiation of Polynomial functions
A polynomial function is differentiated term by term.
Example
If f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 − 4x + 6
then f '(x) = 6x2 + 6x − 4
A function containing brackets must be expanded before differentiating.
Example
If y = (x + 2)(x − 3)
Expanding y = x² − x − 6
![]() = 2x − 1
= 2x − 1
Differentiation of Fractional Indices (Roots)
Roots such as √x can be written as ![]() . This can now be differentiated as normal.
. This can now be differentiated as normal.
If f(x) = √x = ![]()
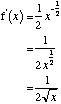
Differentiation of Negative Indices
Terms such as ![]() have to be written as x -2. This can now be differentiated as normal.
have to be written as x -2. This can now be differentiated as normal.
If y = ![]() = x -2
= x -2
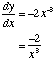
Differentiation of Rational Expressions
Expressions involving fractions may need simplifiying or cancelling first
|
Example 1
|
Example 2
|
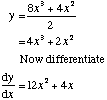 |
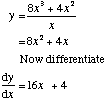 |