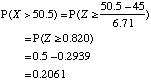The normal distribution can be approximated to the Poisson distribution when λ is large, best when λ > 20.
The Poisson distribution tables usually given with examinations only go up to λ = 6.
As λ increases the distribution begins to look more like a normal probability distribution.
 Note that because Poisson values are discrete and normal values are continuous a continuity correction is necessary.
Note that because Poisson values are discrete and normal values are continuous a continuity correction is necessary.
The values of the mean and standard deviation needed for the normal distribution are μ = λ and σ = √ λ
To summarise:
|
For large values of λ the normal distribution approximates the Poisson distribution
|
|
| Test |
λ > 20 |
| New parameters |
μ = λ σ = √ λ |
Example
In a factory there are 45 accidents per year and the number of accidents per year follows a Poisson distribution. Use the normal approximation to find the probability that there are more than 50 accidents in a year.
Solution
Because λ > 20 a normal approximation can be used.
Let X be the random variable of the number of accidents per year.
To find P(X > 50 ) apply a continuity correction and find P(X > 50.5)
For the normal approximation μ = λ = 45 and σ = √ λ = 6.71 (to 3 s. f.)
The probability that there are more than 50 accidents in a year is 0.2061