This topic contains material that is usually studied in later years, but continues on from the topics covered previously.
Pythagoras' Theorem
Pythagoras' Theorem is a formula which connects the sides of a right-angled triangle.
In words, it states that if you square the lengths of the two shortest sides of a right-angled triangle and add them together the result is equal to the square of the length of the longest side (the hypotenuse).
|
A right-angled triangle
|
Pythagoras' Theorem
|
|
|
|
|
Example
|
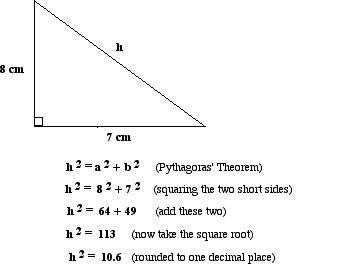 |
Area of Triangles and Quadrilaterals
The area of triangles can be given by a formula:
| Area
|
= 0.5 × base × height
= 1⁄2 × b × h
= 1⁄2bh
|
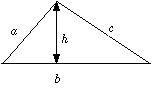 |
The formulae for the area of three common quadrilaterals are given below:
|
Shape
|
Name |
Area |
|
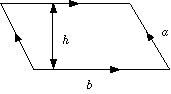
|
Parallelogram |
A = base × height = bh
|
|
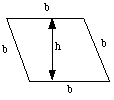
|
Rhombus |
A = base × height
= b × h
or
A = 1⁄2 × (product of length of diagonals)
|
|
|
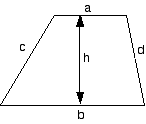
Trapezium |
A = 1⁄2 × ( a + b ) × h |
Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
A prism is an object that has the same shape (or cross-section) for its whole length.
The volume of the prism equal to the area of the cross-section multiplied by the length.
Below are two common prisms, the triangular prism and the cylinder.
|
Solid
|
Name
|
Volume
|
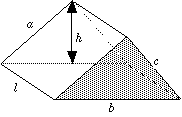 |
Triangular
Prism
|
V = (shaded area) × l
= ( 1⁄2 × b × h ) × l
|
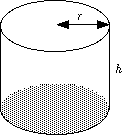 |
Cylinder
(circular prism)
|
V = (shaded area) × h
= ( π r2 ) × h
= π r 2h
|