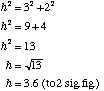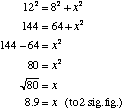The Theorem of Pythagoras is an equation connecting the longest side of a right-angled triangle (called the hypotenuse) with the other two sides.
The Theorem of Pythagoras is an equation connecting the longest side of a right-angled triangle (called the hypotenuse) with the other two sides.
It can be used to find the length of one side of a right-angled triangle given the other two sides.
It applies only to right-angled triangles.
Pythagoras Theorem
The theorem of Pythagoras states that in a right-angled triangle the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two other sides (the two shorter sides).
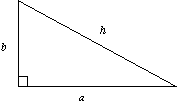 h2 = a2 + b2
h2 = a2 + b2
Note: h, the hypotenuse is always opposite the right angle.
The converse of the theorem is also true
i.e. If h2 = a2 + b2 , then the triangle is right-angled.
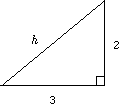 |
|
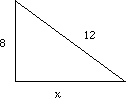 |
|
Pythagorean Triples
A Pythagorean triple is a set of numbers that satisfy the Pythagoras equation, given above.
Some common ones are {3, 4, 5}, {5, 12,13} and {7, 24, 25}. These should be memorised.
Multiples of these triples also obey Pythagoras' Theorem.
e.g. {6, 8, 10} and {9, 12, 15}