Gradients
|
The gradient of a straight line is a measure of how steep it is. The gradient of a straight line is constant for any point on the line.
|
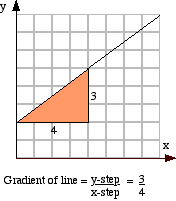 |
|
The gradient of a curve at any point is given by the gradient of the tangent at that point. The gradient of a curve is different at each point on the curve.
|
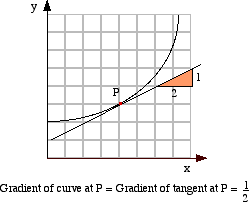 |
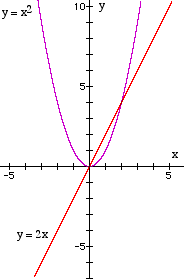
The Gradient Function of y = x²
Consider the curve y = x². Investigate the gradient at various points. (Worked out by finding the slope of the tangents as above.)
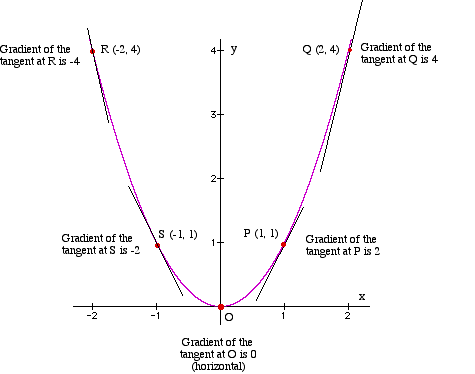
The gradients themselves form a function:
|
x
|
Gradient
|
|
-2
|
-4
|
|
-1
|
-2
|
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
2
|
|
2
|
4
|
 The equation of this function is y = 2x.
The equation of this function is y = 2x.
This function is called the gradient function and from it the gradient of the curve y = x² can be found at any point, for any value of x.
The gradient function is sometimes called the derived function or the derivative.
In the next topic, a non-graphical method of finding the derived function will be shown. This process is called differentiation.
Here are three functions (in pink) and their gradient functions (in red).
|
Function is y = x²
|
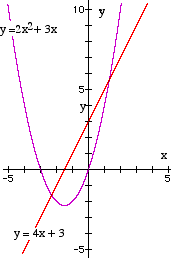
Function is y = 2x² + 3x
|
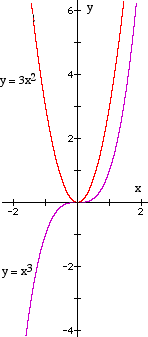
Function is y = x³
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Gradient function is y = 2x
|
Gradient function is y = 4x + 3
|
Gradient function is 3x²
|
 "Can you see the algebraic connection between the function and the gradient function, before the next topic?
"Can you see the algebraic connection between the function and the gradient function, before the next topic?