 There are some rules and formulae that are useful when problem solving using trigonometry.
There are some rules and formulae that are useful when problem solving using trigonometry.
Identities
An identity is an equation which is true for all values of the variable.
They are studied in more detail in Year 13.
Tangent Identity
A useful formula is the relationship between the sine, cosine and tangent ratios.
|
|
Squared Identity
Another useful identity connecting the sine and cosine ratios.
|
sin2x + cos2x = 1
|
Angle Identities
There are a couple of identities which connect the sines and cosines of angles less than 90°.
These can be verified on a calculator.
|
sin x = cos(90 − x) cos x = sin(90 − x) |
|
cos 10°
|
= | 0.9848 |
|
sin (90 − 10)° = sin 80°
|
= | 0.9848 |
Special Triangles
Angles such as 30°, 45° and 60° are used frequently and the trigonometric ratios of these angles are obtained from the two triangles below and it would be useful to memorise them.
|
Top triangle
|
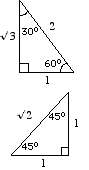 |
sine
|
cosine
|
tangent
|
|
| Half of an equilateral triangle of side length 2 units. |
30°
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bottom triangle
|
45°
|
|
|
1
|
|
| An isosceles triangle with equal sides of length 1 unit. |
60°
|
|
|
√3
|