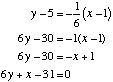The gradient of a curve is given by finding the gradient of the tangent to the curve at that point.
By differentiating and finding the derived or gradient function we obtain an equation which will give the gradient at any point on the curve.
Finding the gradient at a point on a curve
To find the gradient at a particular point on the curve of the function f(x):
Step 1 Differentiate the function to find f '(x)
Step 2 Substitute the x value of the point into f '(x)
|
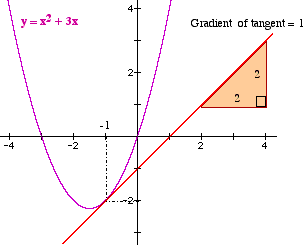
Example Find the gradient of the function f(x) = x2 + 3x at the point (-1. -2) Differentiate f '(x) = 2x + 3 Gradient at x = -1 is f '(-1) = 2 × -1+ 3
The diagram shows this answer. |
 |
Further example
Finding the Equation of the Tangent to a Curve
Once the gradient of a tangent to a curve has been found, the formula y − y1 = m(x − x1) can be used to find the equation of the tangent.
Example
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve f(x) = x2 + 5x at the point (3, 24)
Differentiating f '(x) = 2x + 5
Substitute x = 3
f '(3) = 2 × 3 + 5 = 11
Using y − y1 = m(x − x1)
Equation is y − 24 = 11(x − 3)
Re-arranging y − 24 = 11x − 33
y = 11x − 9
The equation of the tangent is y = 11x − 30
Finding the Equation of the Normal to a Curve
The normal to a curve at a point is the line perpendicular to the curve at that point. (m1 x m2= -1)
|
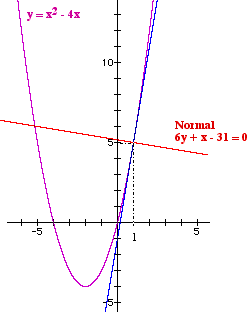
Example Find the equation of the normal to the curve
The equation of the normal is 6y + x − 31 = 0 |
 |