|
The capacity of a container is the amount of liquid that it can hold. Capacity is the volume of liquids. Often the capacity of objects is given using terms like " five spoonfuls".
The metric system has a unit of capacity. It is the LITRE.
Units of Capacity 
The basic unit in the metric system for capacity is the litre, symbol L. (Note this is a capital L.)
The most commonly used units are millilitres and litres.
| Unit |
Symbol
|
Examples |
| millilitres |
mL
|
A teaspoon holds about 5 mL of liquid. |
 |
| litres |
L
|
A large container of milk contains 2 litres.
A standard container of ice cream contains 1 litre.
|
There is an equivalent set of units for measuring volume. This is because containers havevolume and liquids fit in containers.
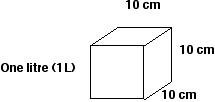
A container with a volume of 1 000 cm3 would hold one litre.
A container with a volume of 1 cm3 would hold 1 mL.
| One litre (1 L) |
1 000 cm3
|
| One millilitre (1 mL) |
1 cm3
|
and
| One cubic centimetre (cm3) |
1 mL
|
| One cubic metre (m3) |
1 000 000 cm3 = 1000 L
|
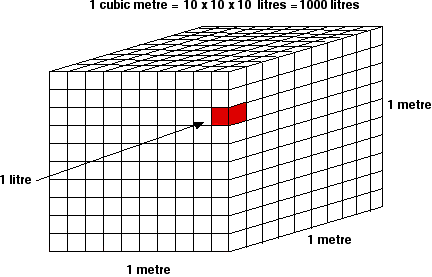
Note that 1 cm3 is sometimes written 1 cc.
Converting between Units
To convert between the units shown in bold in the first column and the units in the second column, multiply or divide by the factors indicated in the third column.
|
Unit
|
Convert to
|
Action |
| millilitres (mL) |
L
|
÷ 1 000 |
|
cm3
|
Stays the same |
|
m3
|
÷ 1 000 000 |
| litres (L) |
mL
|
× 1 000 |
|
cm3
|
× 1 000 |
|
m3
|
÷ 1 000 |
Examples
1. To change 8 litres into millilitres − multiply by 1 000.
8 L = 8 × 1 000 millilitres = 8 000 mL
2. To change 280 mL into L − divide by 1 000
280 mL = 280 ÷ 1 000 = 0.28 L
3. To change 2.1 m3 into litres − multiply by 1 000
2.1 m3 = 2.1 × 1 000 L = 2 100 L
|