Notation
Two lines intersect at A. The intersection of these two lines forms an angle.
The angle formed is written as 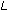 BAC or B BAC or B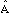 C. C.
The vertex of the angle is always represented by the middle letter.
A single letter can also be used to represent an angle e.g. 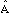 or a or a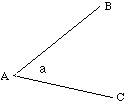
Measurement of Angles
A degree is defined as 1⁄360th of one revolution or turn.
i.e. 360° = one revolution
A minute is defined as 1⁄60th of a degree.
i.e. 1 degree = 60 minutes (1° = 60')
Angles can be measured using a protractor.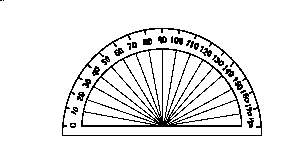
Types of Angles
- Complementary angles add up to 90o.
- Supplementary angles add up to 180o.
- Congruent angles are equal.
- Adjacent angles are next to one another and have a common vertex and line.
p and q are adjacent angles.
Angles that lie within a certain range of values are given special names.
| Angle size |
Name |
Examples
|
|
Between 0° and 90°
|
Acute |
 |
|
90°
|
Right
|
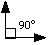 |
|
Between 90° and 180°
|
Obtuse
|
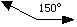 |
|
180o
|
Straight
|
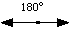 |
|
Between 180° and 360°
|
Reflex
|
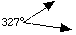 |
Properties of Angles
|
Property
|
Diagram
|
|
Adjacent angles on a straight line add up to 180°
|
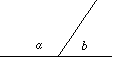 a + b = 180° a + b = 180° |
|
Angles around a point add up to 360°
|
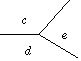 c + d + e = 360° c + d + e = 360° |
|
Vertically opposite angles are equal.
|
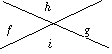 f = g, h = i f = g, h = i |
|