The next two topics cover mathematical modelling, which is a process where mathematical equations are found to fit or approximate real life situations and data. The two most common types of functions which occur in real life situations are exponential functions and power functions. Both processes involve the use of logarithms and you should be familiar with the rules of logarithms covered in the Year 11 topics.
The Exponential Function
The general form of an exponential function can be given as:
y = Aekx
Given a set of values (x , y) from an experiment or survey, the problems are:
- Do these values fit into the exponential model?
- How are the values of A and k found?
To answer these questions, we manipulate y = Aekx using logarithms:
Take natural logs of both sides:
|
ln y
|
=
|
ln Aekx |
|
ln y
|
=
|
ln A + ln ekx |
|
ln y
|
=
|
ln A + kx |
|
ln y
|
=
|
kx + ln A |
This equation can be seen to fit the pattern of a straight line y = mx + c.
This means that from our original set of values (x, y) if we plot (x , ln y) we should get a straight line. If we do get a straight line this confirms that the exponential function y = Aekx is a suitable model and we can proceed to find the values of A and k. The y- intercept of the line will be ln Aand the gradient of the line will be k.
Example
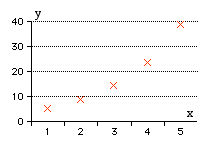
We wish to show that the values in the table below can be modelled using an exponential function:
|
x
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
|
y
|
5.3
|
8.7
|
14.3
|
23.6
|
39.0
|
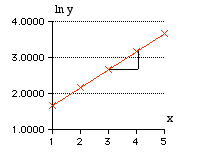
We now take natural logs of each y value and sketch them on a graph to see if they form a straight line. This will be done on a spreadsheet. (Semi -log graph paper could be used. Semi-log graph paper has one axis with a logarithmic scale and the y-value is plotted straight onto this scale − a straight line will result if the exponential model is suitable.)

| The graph of x against y clearly looksexponential. | The graph of ln y against x confirms this − it is a straight line. |
 |
 |
The values will be modelled by y = Aekx.
Remember ln y = kx + ln A
| To find the value of k | To find the value of A |
|
The value of k is the gradient of the straight line. Use any 2 values from the table:
k = 0.50 (to 2 d.p.)
|
The value of ln A is the y-intercept of the graph or can be found using the equation. ln y = kx + ln A ln 23.6 = 0.5.x 4 + ln A ln A = 1.1612 A = 3.19 (to 2 d.p.) |
|
The values can be modelled by the exponential function y = 3.19e0.5x
|
|
Use this simulation to be able to plot log graphs − ![]()
Predicting Values
In the problem above, now that the equation y = 3.19e0.5x has been found, other values can be calculated.
e.g. Find the value of y if x = 8.
y = 3.19e0.5x8
y = 174.2 (to 1 d.p.)