Representation of Decimals
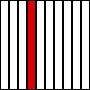
The decimal system is based around the number 10.
|
If 1 is divided into 10 equal parts, each part is called one tenth
|
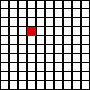
If 1 is divided into 100 equal parts, each part is called one hundredth.
|
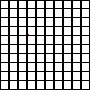
If 1 is divided into 1000 equal parts, each part is called one thousandth.
|
|
|
|
|
|
one tenth = 0.1
|
one hundredth = 0.01
|
one thousandth = 0.001
|
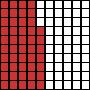
The number shown in the diagram below is shown by the decimal 0.47
Decimals such as 45.92 consist of two parts.
The part of the number in front of the dot (called the decimal point) is a whole number --- 45
The part of the number after the dot is a decimal fraction --- 0.92
![]()
Other examples of decimal numbers are 34.98 and 0.375
Decimals can also be shown on number lines:
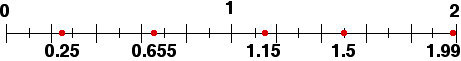
Ordering of Decimals
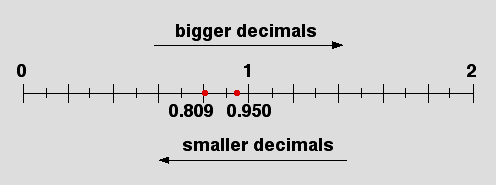
To make it easier to compare the sizes of decimal numbers it is useful to add zeroes.
e.g. When comparing 0.95 and 0.809 write the first number as 0.950
|
0.95
|
0.950
|
950 hundredths
|
0.809 < 0.950
|
|
0.809
|
0.809
|
809 hundredths
|
Types of Decimals
|
Type
|
Description
|
Example
|
||||||
| A terminatingdecimal | one that finishes and has a definite number of digits. |
0.5 or 0.875
|
||||||
|
A recurring orrepeating decimal |
one that has a repeating pattern. |
|
||||||
| A non-repeatingdecimal | a decimal that carries on forever with no pattern. | 0.810675469... does not repeat. |
Rounding Decimals
When an answer works out to a large number of decimal places or the answer does not need to be given so accurately it can be rounded.
e.g. 4 ÷ 7 = 0.571428... goes on forever!
This number can be rounded to a certain number of decimal places.
| 0.571428 can be rounded to : |
0.6
|
rounded to 1 decimal place | the nearest tenth |
|
0.57
|
rounded to 2 decimal places | the nearest hundredth | |
|
0.571
|
rounded to 3 decimal places | the nearest thousandth |
Notice that if you are rounding to, say 3 decimal places, you must look at the next number (the fourth decimal place),
•If this number is below 5 (that is 0,1, 2, 3 or 4) then the 3 decimal place number stays the same.•If this number is equal to, or above 5 (that is 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9) then ADD one to the 3 decimal place number.
e.g. 2.3585 becomes 2.359 when rounded to 3 decimal places.
Operations
Calculators can be used to carry out the following operations involving decimals. However, it is useful to be able to do these basic operations without a calculator.
Adding and subtracting
Make sure that the decimal points are in line. Zeroes can be added to keep places lined up.
|
Calculate:
|
|
|
4.5 + 3.62 |
|
|
2.34 − 0.73 |
|
Multiplying
- To multiply by multiples of 10, move the decimal point to the right.
- When multiplying two decimal numbers, carry out the calculation ignoring the decimal points. Place the decimal point in the answer so that the answer has the same number of decimal places as the total number of places in the two numbers being multiplied.
|
Method
|
||
|
Calculate:
|
||
|
0.27 × 100 |
|
Move point two places to right. |
|
3.4 × 1000 |
|
Move point three places to right. |
|
0.7 × 0.6 |
0.7 × 0.6 = 0.42 |
Two decimal places in question − two in answer. |
|
2.6 × 7 |
2.6 × 7 = 18.2 |
One decimal place in question − one in answer. |
|
1.3 × 1.2 |
1.3 × 1.2 = 1.56 |
Two decimal places in question − two in answer. |
Note: In a whole number, the decimal point comes after the last digit. e.g. 34 means 34.
Division
- When dividing by multiples of 10, move the decimal point to the left.
- When dividing two decimal numbers, write the calculation as a fraction.
- Move the decimal point in both the numerator and the denominator the same number of decimal places needed to make the bottom line into a whole number. Then carry out normal division.
|
Method
|
||
|
Calculate:
|
||
|
(a) 16.5 ÷ 10 |
(a) |
Move point one place to left. |
|
(b) 152 ÷ 100 |
(b) |
Move point two places to left. |
|
(c) 31.5 ÷ 5 |
(c) |
Keep decimal points in a line. |
|
(d) 34.56 ÷ 0.4 |
(d) |
Multiply top and bottom by 10 to make denominator aWHOLE number. |
|
Application
|
|||||||||||||
|
The following scores are recorded in the first round of a gymnastics competition.
(i) What is the total of the marks for the four competitors? (ii) What is the difference between the leader and the person in second place? (iii) If Stevenson scored exactly the same mark for the next three rounds what would be her total score for the four rounds? (iv) What is the average score for the first round? |
 |
(i) The total marks
(ii) The difference
(iii) Total for 4 rounds = 9.56 × 4 =38.24 (iv) Average = total ÷ 4
|
|||||||||||