Types of Symmetry
Types of Symmetry
There are two types of symmetry: line symmetry, which involves reflection , and rotational symmetry, which involves rotation.
|
Type of symmetry
|
Explanation
|
Example
|
| Line Symmetry |
A figure has a line of symmetry if it maps or folds onto itself under reflection in the line.
|
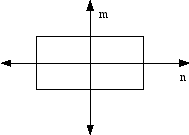
A rectangle has two axis of symmetry.
|
| Rotational Symmetry |
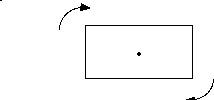
A figure has rotational symmetry if it maps onto itself as it is rotated about a point at its centre. All figures have an order of rotational symmetry of at least 1. The order of rotational symmetry is the number of times the shape maps onto itself during a rotation of 360°. |
A rectangle has an order of rotational symmetry of 2.
|
| Total Order of Symmetry |
The total order of symmetry = number of axes of symmetry + order of rotational symmetry. |
A rectangle has total order of symmetry of
|
The table shows the symmetry properties of some common shapes.
|
Scalene triangle |
|||
|
Isosceles triangle |
|||
|
Equilateral triangle |
|||
|
Kite |
|||
|
Trapezium |
|||
|
Isosceles trapezium |
|||
|
Parallelogram |
|||
|
Rhombus |
|||
|
Rectangle |
|||
|
Square |
|||
|
Regular pentagon |
|||
|
Regular hexagon |
|||
|
Regular octagon |
A figure has point symmetry if it maps onto itself under a rotation of 180° (a half turn). e.g. A parallelogram.
Click here to test your knowledge of quadrilaterals and triangles.
Tessellations
A tessellation is a pattern where shapes are tiled to fill in all of the available space.
Some examples of tessellations:
|
Shapes
|
Tessellation
|
Shapes
|
Tessellation
|
|
|
Triangles
|
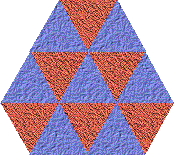 |
Squares and octagons
|
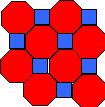 |
|
|
Quadrilaterals
|
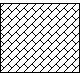 |
Combined shapes
|
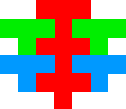 |
|
|
Hexagons
|
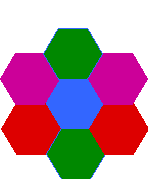 |
Curves (This shape would tessellate!) |
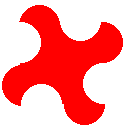 |